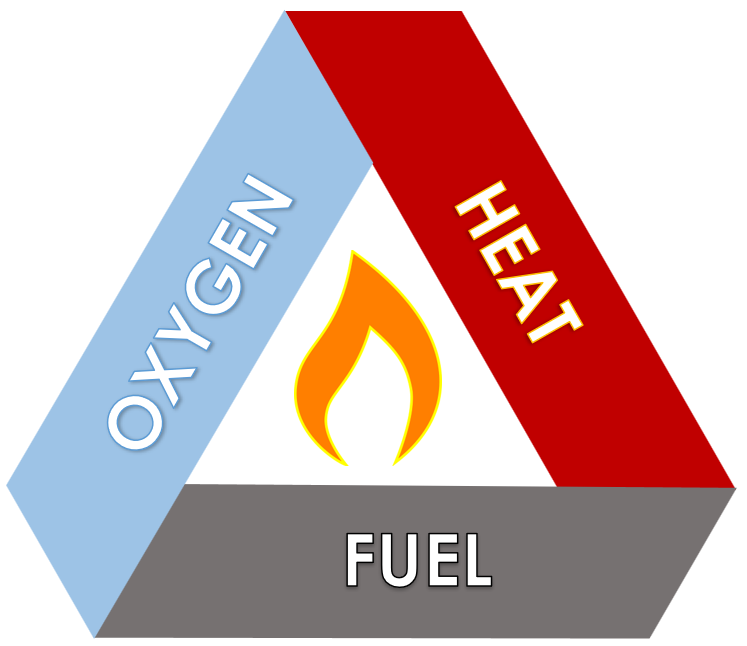
Firstly, let's talk about heat. Heat energy acts as the ignition source for a fire. It provides the energy needed to start the chemical reactions that result in combustion. Without sufficient heat, the fuel will not be able to reach its ignition temperature and thus cannot catch fire.
Next comes fuel - the combustible material that feeds the fire. This can range from flammable liquids and gases to flammable solids like wood, paper, and cloth. Fuel is the different materials that sustain the fire once it has been ignited by heat. It undergoes pyrolysis, breaking it into volatile gases that can be ignited and burned.
Lastly, we have oxygen - an essential component for combustion to occur. Oxygen is present in the air around us. Oxygen, or an oxidising agent, combines with a burning fuel to cause a combustion reaction that produces heat, light, and by-products like smoke and ash.
How Does the Fire Triangle Work?
Together, heat, fuel and oxygen create a self-sustaining chain reaction known as the Fire Triangle. Without these components, a fire cannot start or continue burning.
When all three components of the Fire Triangle are in the right proportions, a fire can quickly spread and become dangerous. This is why taking precautions to minimise the risk of fires is essential by removing or controlling one or more of these elements.
For example, reducing fuel availability can help prevent fires from starting or spreading. Proper storage and disposal of flammable materials are crucial in minimising the potential hazard. The risk of a fire starting can be significantly reduced by keeping fuel sources away from possible ignition sources, such as heat or open flames.
Similarly, controlling the oxygen supply can also help mitigate fires. In certain situations, like in enclosed spaces or storage areas, limiting the amount of oxygen present can prevent combustion from occurring. This is why it is common to find fire suppression systems that use chemicals or gases to displace oxygen and suppress fires.
Potential Sources of Heat, Fuel, and Oxygen in the Workplace
Identifying potential sources of heat, fuel, and oxygen in the workplace is crucial for fire prevention. By understanding these elements and their interactions, we can take proactive measures to minimise the risk of fires.
Heat sources can vary widely depending on the nature of the work environment. It could be anything from electrical appliances and machinery to open flames or friction from moving parts. Regular maintenance, proper insulation, and ensuring that heating elements are kept away from flammable materials effectively reduce the chances of a fire starting.
Fuel sources refer to any material that can burn. This includes apparent combustible materials such as gasoline and wood and less obvious ones like paper, fabric, or dust. It is essential to properly store and dispose of these materials to prevent them from becoming fuel for a potential fire. Keeping work areas clean and clutter-free can also minimise the risk of accidental ignition.
Oxygen, the third element of the fire triangle, is almost always present in the ambient air. However, there are situations where controlling the oxygen supply can be crucial in fire prevention. For example, reducing the amount of oxygen in confined spaces or storage areas can significantly reduce the likelihood of a fire. Starving the fire of oxygen can be achieved through suppression systems that displace oxygen with gases such as carbon dioxide.
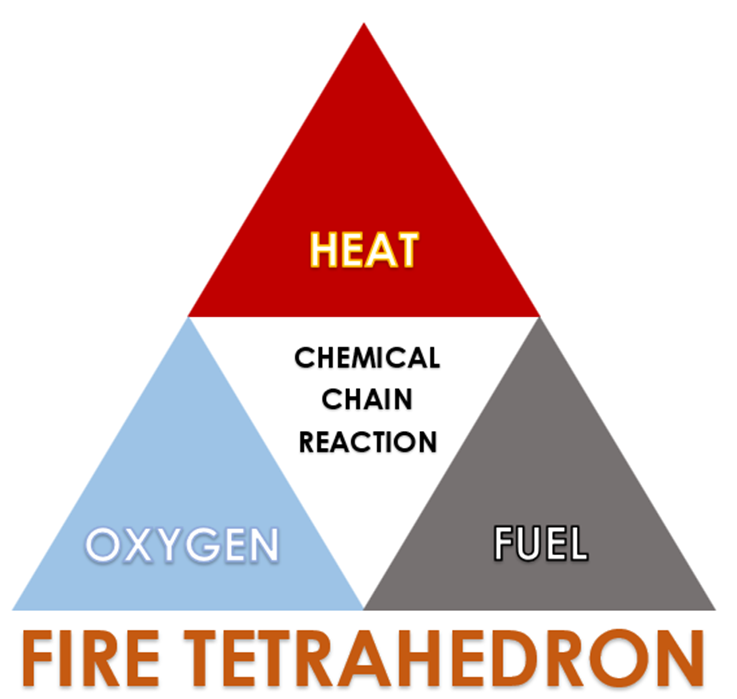
What is the Fire Tetrahedron?